As we begin 2026, businesses need to constantly work on their pricing strategies to remain competitive in the rapidly changing ecommerce industry, where incidents come from all directions, such as tariffs and AI initiatives. Since pricing directly influences your market position and profitability, it is necessary to implement the right competitive pricing strategies to attract customers successfully and keep up with the ecommerce market trends.
In this fast-paced ecommerce market, businesses must identify new trends and happenings almost instantly and adjust their businesses to fit them. Here are some ecommerce pricing strategies to consider for 2026 and beyond, along with guidance on choosing the most suitable one for your business.
Prisync Training Hub #9 | 6 Common #Pricing Strategies – #Ecommerce #Pricing Program
Let’s break it down a bit further:
1. Psychological Pricing Strategies
Psychological pricing is a powerful strategy for businesses that leverages consumer psychology to increase their sales and revenue. The key to implementing this strategy is understanding customer psychology, and the next step is making prices more appealing and influencing customers’ perceptions, nudging them to purchase your products. Here are a few techniques:
Charm Pricing
We all have seen this one, a price tag with a .99 ending. Setting a specific price for a product with decimals can make the price seem significantly lower, mitigating the decimals as if the ending part doesn’t matter.
Best Plays by Prisync Players #3: Rounded Prices 🏷️ 🏓
Price Anchoring
Placing a higher-priced item next to the one you want to sell can make the latter appear to be a better deal, as customers are influenced by the higher initial price displayed in the first place.
Bundle Pricing
It is typical for businesses to bundle complementary products, such as showing an air fryer with a cookbook or accessories. Bundle pricing means offering products in a bundle at a lower price, whereas they would be individually expensive. This can increase the perceived value of your products and encourage higher spending.
Other small tactics can be related to visual display, since removing the dollar sign and using smaller price fonts and distinct colors can help lessen the perceived impact of a product’s price. These psychological pricing techniques rely on common cognitive biases, making customers feel they are getting a better deal or more value for their money and influencing their purchasing decisions. However, these tactics may lose their effects if the consumer becomes aware of them, so they must be implemented through careful contemplation.
2. Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing is a pricing approach that allows merchants to simultaneously use flexible and momentary prices based on market demand, competitors’ prices, and seasonality. It is also beneficial in rapidly changing ecommerce markets where prices can change quickly. Its flexibility allows businesses to respond to market changes dynamically since consumers often compare prices from multiple sellers before purchasing, which lets merchants remain competitive while gaining profits. Here are some of the advantages of dynamic pricing:
If you are selling highly competitive products where the profit margins are considered to be low, then dynamic pricing automation is helpful for your business. With dynamic pricing, you can target different customer segments with different buying abilities or even categorize your products and improve several pricing strategies according to each category.
Prisync Training Hub #8 | What is a #DynamicPricing Strategy? – #Ecommerce #Pricing Program
We know that manual price tracking is impractical, and if you rely on pricing engines to retrieve your prices, your pricing adjustments will only be as good as the data you receive. Pricing software like Prisync helps you easily control your market position with predefined rules since it will gather all the necessary market information with robust data analytics capabilities.

3. Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing is setting the selling price of your product or service by adding your desired markup on top of the production cost. This method aims to cover all your expenses with a clear profit percentage, making cost-plus pricing one of the most straightforward methods.
Even though cost-plus pricing seems like a good option for businesses with precise cost structures, this strategy may not always maximize profits, especially in highly competitive markets where you can’t know how your position is against your competitors. Thus, this strategy hinders your business’s competitive capabilities. Watch our Cost-Plus Pricing Strategy video to find out why Fitbit is able to charge a lot more than the alternatives.
Prisync Training Hub #5 | Cost-Plus Pricing Strategy – Ecommerce #Pricing Program
4. Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing is an approach that allows businesses to set prices based on the customer’s perceived value rather than the cost of production. Product differentiation and a strong brand image are key to this strategy since consumers will be willing to pay for your products. You can justify higher price tags by assessing what customers value in your products or services.
While luxury buyers focus on exclusivity, cost-conscious consumers focus on price, which can help you classify your product catalog, where perceived value will differ for each customer segment. Understanding what customers value most about your product allows you to price it according to its perceived benefits.
5. Economy Pricing
Economy pricing is a strategy of setting prices low for products or services to attract price-sensitive consumers. This strategy is common in grocery stores where production costs are low, and sellers aim to maximize sales volume and market share rather than focus on high-profit margins per unit. For example, at Costco, you can find lots of items from well-known brands as well as their exclusive Kirkland Signature line of products. By selling Kirkland Signature, price-sensitive customers will return to Costco to buy large quantities of products, and the affordable prices will also attract new customers.

It is crucial for businesses to have low production costs to maintain this pricing structure since the profit margins are also typically low. In order to keep production costs low, companies need to simplify their operations by optimizing supply chains and reducing overhead costs.
Even though economy pricing is a great option when entering new markets or competing against higher-priced alternatives, it also holds a risk of being perceived as low-quality because of the low price points, which will impact brand perception.
6. Freemium Pricing
Freemium pricing is an approach where businesses offer a free version of their product with fewer features to attract a customer base for the app and encourage them to pay for premium features. This strategy is especially popular in software and digital services such as Spotify, Zapier, and Canva.
As users become accustomed to the free version, many may want to transition to paid plans for additional features and benefits. Freemium pricing can be a great strategy for growing a larger user base, and the word free feels like music to customers’ ears. Yet, companies should emphasize the value of each free and premium offering since it can be harder for businesses to upsell their services.
7. Competitive Pricing
Competitive pricing is a strategy where businesses price their products with the competitors’ prices in mind, which means companies need to constantly assess their competitors’ prices to have the most optimal price and offer the best deal to their customers.
Prisync Training Hub #6 | What is Competitive Pricing? – Ecommerce #Pricing Program
The aim here is to outprice your competitor, but is it always better to be the cheapest in your market? Definitely not. Being the most affordable can hurt your business with reduced profits. Competitive pricing requires thorough market research to define your business objectives.
According to your business objective and the current market dynamics, you can determine how you want to position yourself. Finding a competitive and profitable price is crucial for the sustainability of your cash flow. In order to keep up with the competition, you can set your prices equal, a little lower than, or a little higher than your competitors.
8. Price Skimming
Price skimming is a pricing strategy where companies can skim the layers of the market by setting a high initial price for a new or innovative product to capture high profits from early adopters who are willing to pay for a premium product and gradually lower the price over time to attract price-sensitive buyers as well. With this approach, companies can gain revenue at each price point from customers with varying willingness to pay.
One advantage of price skimming is that companies can cover their research and development expenses while developing the product or service from early adopters when the product is in its early lifecycle. Also, price skimming can help brands create a higher-end brand image perception, leading to customer loyalty, although competitors can introduce similar products after the launch of your products.
Price skimming is also risky if your competitors are too fast to produce similar products, since lower-priced alternatives will capture the price-sensitive consumers’ attention, or if you drop your product prices soon after the launch, early adopters may feel alienated by the price change. The key to implementing a successful price skimming strategy lies in emphasizing the value and quality of your product while establishing a strong brand image.

9. Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing is a predetermined approach for entering a new market or introducing a new product into their existing catalogs by offering low prices or discounts on your services or products for a specific time to attract new customers. It is the best strategy when introducing a new product since low prices will attract customers if you aren’t an established business in the market.
Businesses can increase their market share among competitors by implementing penetration pricing, which allows them to see the demand and raise their prices over time. For example, Netflix was affordable when it first entered the streaming market and managed to compete against the DVD rental industry by implementing penetration pricing.
10. Loss-Leader Pricing
Loss leader pricing is the key concept behind using a low-priced item to draw customers into the merchant’s store. Once the customers are engaged with your store’s offerings, the objective is to nudge them to purchase other products at regular prices as well. This strategy relies on people making more supplementary purchases. The most common example is introducing the main product at a reasonable price, knowing the customers will return for replacement or add-on products. For example, if you have bought a Nespresso coffee machine, you will most likely get their coffee capsules on a regular basis. So, loss leader pricing is an excellent strategy for increasing customer loyalty, profits, and market share among competitors.
11. Premium/Prestige Pricing
Prestige or premium pricing is a pricing strategy of setting prices higher than the market average for exclusive products. With this strategy, brands aim to convey a sense of superior quality and exclusivity to build a premium brand image.
Prestige pricing can be effective in two situations:
1. When your brand has a premium feel and luxury manufacturing, whether it’s a bag, pen, or wristwatch. The differentiated value of your products can justify the higher prices since they are truly high-quality and exclusive.
2. When you are entering a market with a demand for your product, but without any specific competitors at the moment. Since your product is unique, customers are willing to pay more for it because there are no other options available, and premium buyers value exclusivity.
12. Keystone Pricing
Keystone Pricing is a very straightforward pricing strategy of doubling a product’s actual wholesale or production cost and setting it as the new price of your product’s retail price. This means that 50% of the retail price is profit for every item sold. Keystone pricing is easier and more reasonable for generating higher profits if you have a unique product catalog.
The problem with the keystone strategy is that it doesn’t work well on competitive products that are commonly available. We know that customers compare prices before making their purchasing decisions. When they see a cheaper option for a similar product of the same quality, they will most likely prefer the considerably more affordable option.
On the other hand, if you have managed to differentiate your product offering with its quality and have done a successful branding for your company, or you believe that your product is rare and in high demand, then implementing keystone pricing makes sense for your products, and people are more willing to pay for them.
13. Multiple Pricing
Multiple pricing, or multiple unit pricing, is a pricing strategy that lets you sell identical products in a bundle, allowing you to sell more in terms of quantity. For example, this tactic is widely seen in grocery stores, whether it is cereals, sodas, or detergent packs, just to name a few.
Let’s think of it this way. If you put an option of a can of soda in a bundle of six, there will be a variety in the market and a whole customer segment that this option will entice. Thus increasing the chance of selling more products at different price points.
14. Ladder Pricing
Ladder pricing, much like the name suggests, is a strategy of offering different versions of a product, each with a different set of features and benefits for various price points. For example, a company that sells software can provide a basic service with limited features, a mid-tiered option with a team plan, or a full premium service with unlimited features, each at a different price.
One disadvantage of ladder pricing is that it is harder to convince customers to upgrade to an upper, more advanced version, leading to lower sales of the premium versions. In that scenario, companies must focus on value differentiation and make sure that the customers understand this differentiation to justify higher prices for each segment, eventually allowing each customer group to choose between options according to their budgets and needs.
15. Discount Pricing
Discounts are a great way to drive traffic to your stores and help you move excess stock, increasing sales of more items. Discount signs attract many customers to your store, but if you are discounting your store’s best sellers, then you are cutting into your own profits.
To implement a successful discount pricing strategy, you must determine your business goals properly. You can aim to sell out a particular line of products, enhance customer loyalty, attract as many customers as possible during seasonal events, or simply increase your earnings.

16. Flexible Pricing
Flexible pricing relies on changing the price of your products or services according to the demand and market conditions via negotiating between merchants and consumers. Dynamic pricing, as a subset of flexible pricing, allows online businesses to adjust their prices in response to market demand – think of an airline company and how they increase their prices before the holiday season. Another flexible pricing example is market-based pricing, where the price for a product is set based on similar products or the level of competition in that specific market, as well as the fluctuation in demand. This strategy is common in grocery stores where customers see lots of alternatives to each product.
Much like its name suggests, usage-based pricing is a flexible pricing strategy where customers are charged as the consumption of the service or product increases. One advantage of this strategy is that customers are free to determine their usage, and every customer is different. For example, an image or voice generator app can sell credits for each piece, and the customers don’t have to have fixed subscriptions to engage with the app’s services.
Sometimes, a business can have specific needs, and some service or product providers can fulfill the business’s needs, but haven’t yet determined a fixed price for the type of service you need. Then, it is common to negotiate between companies to decide on pricing. Negotiable pricing is widely standard among SaaS providers and B2B businesses.
17. Distribution Pricing
Distribution pricing is the price of the products or services that the main suppliers determine to convey to the distributing vendors. The distribution price is naturally lower than the retail price since the vendors also have to make a profit from the items as well.
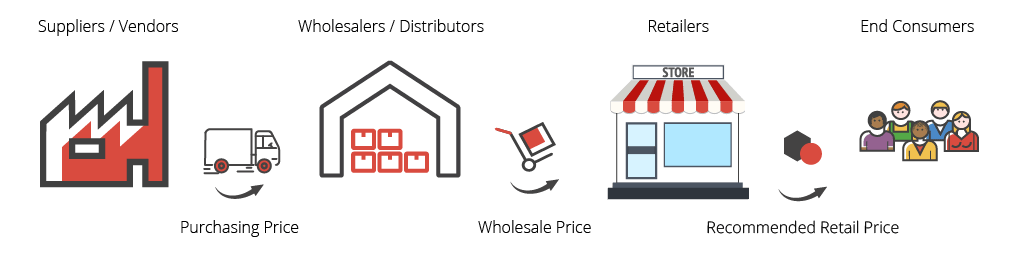
The key here is to balance your distribution price so that it is not too high or too low. If you price yourself too low to be competitive, then you are hurting your own profit, and if you price too high, the vendors can replace your products with a more affordable supplier.
18. Hedonic Pricing
Hedonic pricing is a pricing strategy that takes both external and internal factors into account. It is common in industries such as housing markets where external factors may become as important as the item’s quality. Hedonic pricing is set according to people’s willingness to pay, which can be both advantageous and disadvantageous. Let’s continue from the house example, a house can have great internal features such as a fireplace, an excellent kitchen, or a solar-panel system, but if there’s nothing surrounding the house or if the neighbourhood is not safe, the price of that house will be significantly lower.
19. Price Variance
Price variance is commonly used in yearly budget preparations to decide if inventory or additional costs need to be adjusted accordingly. This means that the actual costs may be more than the budgeted, which is undesirable for businesses. So, price variance is considering all the expected expenses on top of the actual cost of an item. Companies can calculate price variance for materials, labor, fixed, and variable costs, which can fluctuate over time, eventually affecting the quantity of the items that will be ordered.
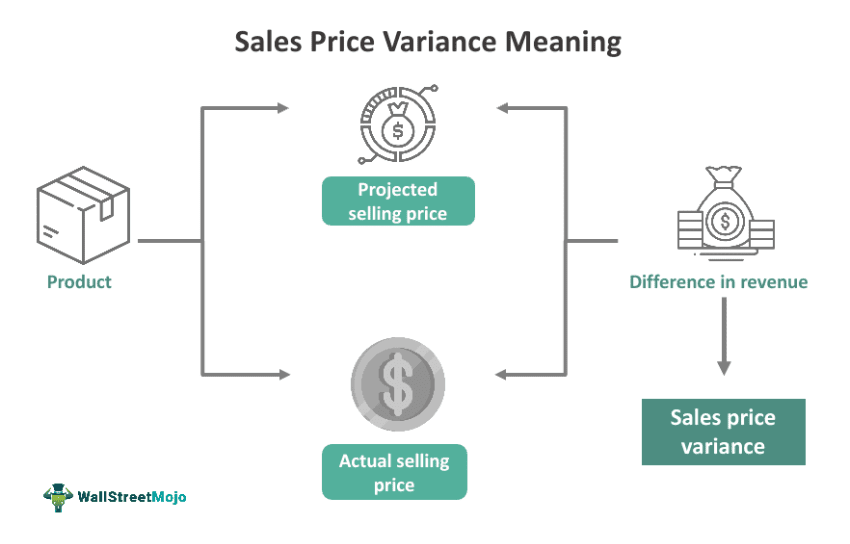
20. Price Waterfall
Price waterfall is a visual parameter that shows each factor that goes into the price of the product or service, aiming to show where the profits are coming from. It is important to understand price waterfalls since it is essential when managing revenue, as the indirect costs of producing products may not be the same while producing products in different quantities.
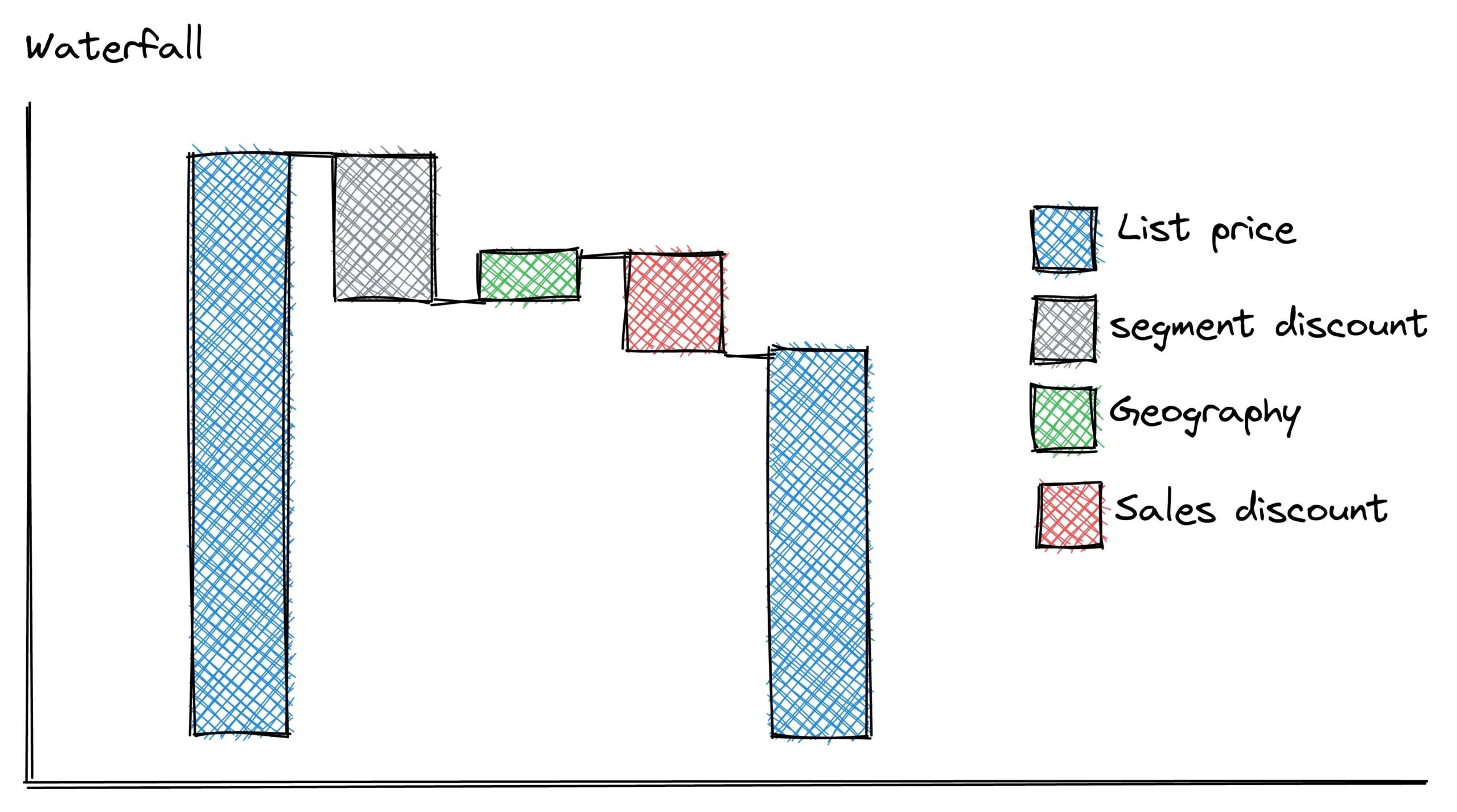
Another advantage of the price waterfall is that it helps businesses identify if there is a profit leak in the revenue they are receiving. Assume the product’s direct costs are stable, but the seller is changing some parameters, such as discounting or offering promotional products, which will directly affect the profit amount.
21. Uncommon Pricing Strategies
While some businesses may be fine with common pricing strategies, exploring not-so-common ones can differentiate your brand’s offering and create unique value propositions. Let’s check:
Pay What You Want
In this strategy, customers pay according to what they think about the product’s worth, which sometimes means getting no money from the buyers. This approach is primarily used for charitable or social purposes and can foster trust and increase customer loyalty since it is based on consumers’ ability to pay.
Subscription-Based Pricing
This strategy consists of offering products on a subscription basis that ensures steady revenue for the business and increases customer retention, leading to long-term customer relationships.
Geo-Targeted Pricing
This pricing strategy relies on adjusting prices based on the geographic location of each customer, which helps businesses maximize their profits in different markets with tailored offerings.

How to Pick the Right Pricing Strategy
We have examined a whole lot of pricing strategies, but how can you choose between the strategies you want to implement? The most essential part of the process is selecting the one that will benefit your business the most. There are several points to consider when choosing the right pricing strategy for your business. Let’s check some of them!
1. Understand Your Market
Companies need to conduct extensive market research to understand the competitive landscape, customer behaviors, and asses their business goals, streghts and weaknesses to adjust their pricing strategies.
2. Analyze Costs and Margins
The second step is to ensure that the chosen pricing strategy covers your costs and achieves the desired profit margins. You need to consider how much it costs to produce the product or service to sell in your store. After calculating all your costs, including production, inventory, employee, etc., you need to decide on a profit margin that will keep you competitive and profitable.
3. Customer Value Proposition
The next step is to match your pricing strategy to the value you offer from your product or service. Each customer segment looks for a different value proposition, but they all need to believe your product is worth buying. To figure out what the customer perception would be, you need to consider what value they could give to your products and reflect it in your pricing according to your brand image.
4. Test and Iterate
After you have decided on a good pricing strategy, you must constantly test your prices to refine your approach. Frequent testing helps determine if you are benefiting and getting the profits you look for, or losing sales from your chosen strategy. If your business is not on the right path, you might consider revisiting your business goals or trying a different pricing strategy.
Prisync Training Hub #11 | Common Pricing Mistakes – Ecommerce #Pricing Program
Conclusion
In 2026, businesses need to be agile and innovative in their pricing strategies to remain competitive. Understanding and utilizing various pricing models can help you optimize pricing to increase sales and profitability. This is not a one-solution-fits-all situation here. But, it’s crucial to carefully research and evaluate your market, costs, and customer value in order to choose the strategy that best aligns with your business goals. We have delivered a complete guide that will help you decide which strategy suits you the most, keeping in mind that every business’s needs will be different and every ecommerce journey will be unique. Regardless of your business type, considerautomating the pricing process with Prisync to stay competitive in the constantly changing market landscape.
