Companies often begin their production process by estimating a budget based on the number of products or services they plan to sell, the price at which they will sell them, where they will sell the products or services, and whether the promotional efforts will be worth the investment, considering potential profit calculations.
For companies to manage their revenue properly, all the factors we have mentioned need to be nearly on point; however, things can sometimes get complicated. The company may end up selling its products at prices different from those expected at the beginning, which creates a gap between the estimated revenue. The resulting difference is called price variance, and it can be used to your business’s advantage once you grasp the concept.
Before we explore how variable pricing can contribute to revenue and the price variance formula for making informed business decisions, let’s begin by examining what price variance is.
What is Sales Price Variance?
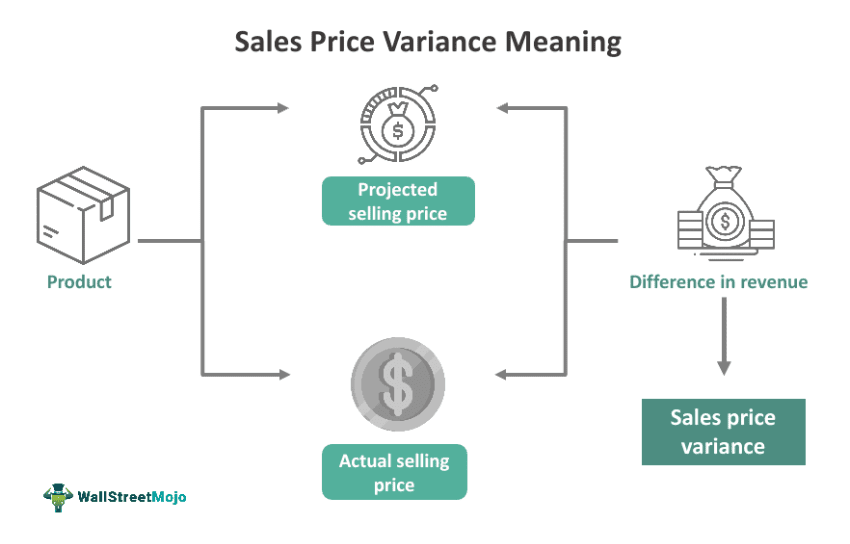
Price variance, also known as the sales price variance, occurs when a company sets a target price for its products or services, but the actual price the company ends up selling differs from this target. Variable prices help companies manage their revenue by identifying which of their products are primarily contributing to their overall profits and which ones require a different pricing approach to increase revenue.
Favorable and Unfavorable Price Variance
Let’s say you’re a cosmetics brand that sells makeup products. You have introduced a lipstick line that changes color according to the pH level of each individual’s skin, and it has created an immense demand, which resulted in increasing the lipstick’s price higher than intended and selling more products at a significantly higher price, which is favorable in terms of sales price variance. The reason behind this increase may be that you have provided a unique benefit to customers and executed a successful promotional campaign for the product.
On the other hand, let’s say you have already promoted a blush line, but the revenue wasn’t quite what you expected, and demand fell; then, you proceeded with a discount on the specific product line to sell the products, which resulted in selling your products lower than expected which is unfavorable in terms of price variance.
Sales Price Variance Formula
Let’s explain the price variance formula using the same example, where we assume you are a merchant selling beauty products, and walk through the formula with the same lipstick and blush line. Let’s say for each line, we have produced the same units, such as 1000 products. The sales price variance is as stated below:
Sales Price Variance = (Actual Selling Price – Budgeted Selling Price) × Units Sold
How to Use Price Variance Formulas
First, we need to get familiar with the concepts of actual and budgeted selling prices. The actual selling price is the amount at which we ultimately sell our product. In this case, we managed to sell our lipstick at a price higher than the budgeted selling price. Let’s say our budgeted price for the lipstick was $5, and we ended up selling it for $7. Additionally, we successfully sold all of the products.
If we subtract the budgeted sales price from the actual selling price, the resulting price difference will give us the price variance, which we can then multiply by the number of units sold. So, the difference in unit price is $2, and since we have sold all of the lipsticks, we will multiply it by 1000. The sales price variance is $2,000, which is favorable.
On the other hand, the blush line we had didn’t receive the demand we expected, but still, we managed to sell all of our products at a lower price. Let’s say our budgeted price for the blush was $8, and we ended up selling it for $3. If we subtract the budgeted sales price from the actual selling price, the difference in unit price is -$5. If we multiply this by 1000, the sales price variance is an unfavorable $5,000.
Material Price Variance
What happens if the price changes at the source and the production costs change accordingly? Just as consumers who choose to buy from another seller when the prices increase or are willing to pay more for that product, the same scenario applies. You can respond to changes in supply by seeking a replacement supplier. Alternatively, if you wish to continue with the same supplier, you may need to calculate the shift in material price variance and adjust your pricing strategies accordingly to protect your profit margins.
Even though labor variance and overhead variances are somewhat pre-calculated, they can also be affected by material price variances or a change in any of the factors can create price variance as well. Recently, with the enforcement of tariffs, merchants who import goods from the US will likely experience cost increases. Therefore, it appears that merchants will need to either increase their selling prices or reduce their profit margins to avoid creating unfavorable price variances. Another point to consider might be reducing the labor and overhead expenses due to the unwanted circumstances.
Material Price Variance Formula
This time, let’s break down the material price variance formula with the tariff example. The material price variance is as stated below:
Material Price Variance = (Standard Price – Actual Price) × Quantity Purchased
The formula is similar to the sales price variance formula, but this time, it is for the materials we purchase. The standard price is the price at which we are buying the products, and the actual price is the pre-calculated and expected price. Let’s say we once purchased a gemstone for one dollar to sell in our gift shop, which specializes in jewelry. After the tariffs, the cost of the gemstone is $1.25, and we want to continue purchasing the same amount, let’s say 300, for each import; the material price variance will be an unfavorable $75. The formula suggests that we either need to increase our price by $0.25 for each piece, change suppliers, or sacrifice $0.25 from our profit margin.
Understanding the material price variance in such circumstances will help you price your products effectively and maintain a market position that aligns with your business goals.
Strategical Approach to Variable Prices
You know that customer demand is a rollercoaster in the competitive ecommerce landscape. If you set static prices, it is soon inevitable that you will hurt your business. Instead, you can try out different price points to see at which price you sell most of your products profitably in different levels of demand.
Variable pricing enables businesses to respond to market changes, and if the change is unfavorable, you can compensate for the loss with swift price adjustments to maintain sales, even if your profit per unit decreases. On the other hand, variable pricing is manageable in ecommerce since price tracking tools, such as Prisync, can help you implement various pricing strategies based on your current market position.
If sellers start to reduce the price of the same product as yours, Prisync will notify you about the price drop. Then, you can monitor a decrease in demand and apply a discount or develop a counter strategy accordingly. Being the most expensive option can leave you at a disadvantage in the competition if you don’t adjust your prices in response to competitors. Another scenario could be that you are the cheapest in the market, and tracking competitors’ prices becomes useful in nudging you to increase your prices to maintain healthy profits.
Wrap Up
Sometimes, the price we estimate for a product and the price we ultimately sell it for differ, which creates a price variance that businesses need to understand to manage their revenue and maintain profitability successfully. It is essential here to leverage favorable price variances and also to address unfavorable price variances, taking the opportunity to evaluate their pricing strategies and implement corrective actions to adapt to market changes swiftly. Understanding your price variance can also help you determine when to use promotional strategies, clear your inventory, or engage in supplier negotiations. Applying price variance formulas correctly can ultimately help you optimize your revenue and remain competitive in a dynamic ecommerce landscape.