Many online store owners flock to search engine optimization as a cost-effective way to bring customers to their websites. However, SEO is not as simple as creating an ad and bidding for placement. Optimizing your site for organic search engine ranking needs to happen on every line of code, from your product descriptions to your website’s security.
Let’s go through the twelve most important items that should be on your SEO checklist when optimizing your eCommerce website for boosting organic traffic and, in return, profits.

1. Register with Google Search Console
Your first step in improving your online store’s SEO is auditing where it currently stands. The best way to do this is by utilizing the Google Search Console: a free tool that shows how Google views your site. The Google Search Console, or GSC, can provide you with important information on how your site performs on their SERPs (search engine result pages), giving you insight on your SEO strategy moving forward.
The GSC can be accessed within your Google account’s Google Webmaster Tools, wherein you can add your site as a property. You’ll also want to submit your sitemap to Google, which will appear in your Sitemaps report.
Within the GSC, you can learn about and monitor:
- Search keywords that you’re ranking for
- Highest traffic pages
- Average CTR (click-through rate)
- Impressions & average position over time
- Ranking increases and decreases
- Highest traffic & CTR queries
- Index and unindexed pages
- Total backlinks on your site
- AMP errors
2. Set Up Google Analytics
While the Google Search Console gives you insight into your site’s overall performance, Google Analytics can provide you an even more detailed view of how visitors and customers are interacting with your site.
To access Google Analytics, set it up with your Google account and add the tracking code to your website. Most eCommerce platforms have a built-in tool that streamlines this process, making it so that you don’t have to manually add the code to every page on your site.
With your account set up, you can start viewing data and learning about your site’s traffic. There are several different types of reports, all falling under four main categories:
- Audience Reports: This includes demographics, interests, geography, and behavior.
- Acquisition Reports: Analyze from all traffic, AdWords, SEO, social, and campaigns.
- Behavior Reports: Monitor behavior on-site content, speed, search, and more.
- Conversions: Track your goals, eCommerce, and multi-channel funnels.
3. Secure Your Site
If you haven’t already, you need to secure your site. This is done with an SSL certificate, which stands for Secure Sockets Layer. But, how does your site’s security affect its SEO? Google cares about their users’ experience browsing sites that their SERPs serves them; this includes their security. Having an SSL certificate installed on your website shows Google (and your customers) that your site is trustworthy and safe to browse and buy from.
Secure websites with SSL certificates will have “HTTPS” at the beginning of their URL. Without security, your site will begin with HTTP. This matters because Google will alert users when navigating to an unsecure site that doesn’t have HTTPS with a “Your connection is not private” notification. This can cause unsecured websites to lose traffic and ranking.

4. Conduct Keyword Research
With all of the basics in place, the next step is formulating your SEO strategy. The heart of any business’s SEO is optimizing for the right keywords. But, before you can do that, you need to find out what the right keywords are. This is where keyword research comes in.
First, you need to understand who your customers are and what they want from your business. This can help you glean what they would type into Google to find your site, what products they’re looking for, and what they already know.
With these brainstormed keywords, utilize a keyword tool like the “Search Results” feature in Google Search Console to see how they perform on SERPs. You can also determine broad matches and exact matches based on Google’s search data. From here, determine which keywords have high volume and relevance to your business.
Remember that you don’t want to target keywords with the highest volume if you’re a smaller business – you may not be able to compete with the sites that already rank for them. To rank for better keywords with high conversion value, look for “long-tail” keywords. This type of Keyword is usually a phrase, question, or several words stringed together that form a more specific query. Here’s an example:
- Broad Keyword: “t-shirt”
- Long-Tail Keyword: “inexpensive red cotton t-shirt”

5. Add Content to Pages
Adding optimized content is one of the most effective ways to help pages on your site rank. In the case of eCommerce, this means adding content to your product pages, category pages, and extra pages like “About Us” or a blog.
Product pages should have valuable descriptions that are unique from the manufacturer’s product description. But, this piece of content needs to be written clearly and concisely. If it lacks readability, then employ the paraphrasing tool for assistance. This doesn’t just serve the purpose of important product details; it can also be used as a form of marketing and optimized with your target keywords. Another form of content that should be available on product pages is a section for customer reviews; this can contribute to your site’s rich snippets and assist in developing social proof.
Like you performed keyword research on your online store, you should also research keywords for each page you’re optimizing.
6. Find Keywords Through Competitor Research
If your competitors rank higher than your ranking in search engines, you can use their sites to get keyword ideas. First, type your primary Keyword in Google search, choose the highest-ranked competitor, and scan their category and product pages for potential keywords.
You should use a different keyword than your competitors because they can outrank you. It’s also critical to pay attention to breadcrumbs. It’s an advanced navigation function that helps Google to scan and index your site. After entering your site into Google, you should see yousite.com > category > subcategory if you’ve set up your breadcrumbs correctly.
7. Optimize Your Meta Tags & Slugs
Meta tags are pieces of text found within a site’s code that describes content on the page. This includes page titles, headings, descriptions, and images.
First, let’s start with the meta title. This refers to the title of your page as shown in a SERP. Your page’s meta title should include the keyword that you’re optimizing for on that page, ideally near the beginning. It should also be easy to read, enticing, and short (Google prefers 50-60 characters.)
Next, optimize your page’s meta description. Here, you’ll want to include your primary target keyword and secondary, relevant keywords. However, avoid keyword stuffing, which is the practice of trying to add as many keywords as possible into a piece of content – this results in a hard-to-read, spammy description that Google will penalize. Keep your meta description within 160 characters, as Google will begin to truncate it past that point.
The heading tags on your site should also be optimized. The site’s H1 tag represents the page’s title, so you should only use one and include your primary keyword. Make sure that your H1 tag is unique from your page title tag. H2 tags, and so-on, are the perfect place to add supplementary keywords.
Images also require meta tags, referred to as “alt tags.” Adding image alt tags helps Google better understand what an image on your page is, but it also helps improve your site’s usability for visitors using screen readers.
Beyond meta tags, optimizing the page’s URL slug is also important. The “slug” of a URL refers to everything after your domain name. Keep your page’s URL slug short, relevant, and unique to the page, and include the target keyword.

8. Use Rich Snippets
Have you ever seen a search result with extra features, like star ratings or prices? Those are rich snippets, which is structured data that is used to add extra details about a site and page content that search engines can use to better display your page.
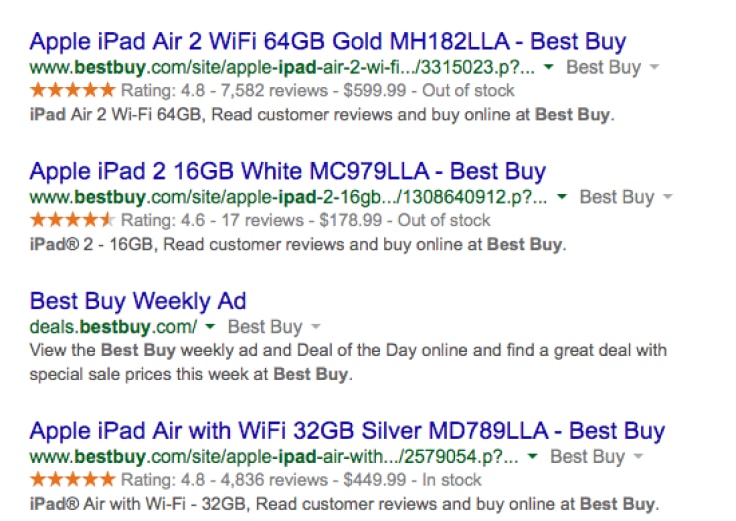
There’s a long list of rich snippets available to use, but the most important ones to optimize for in eCommerce are:
- Pricing: This shows directly on your page’s search result the price of your product.
- Ratings & Reviews: These appear on product page results as star ratings based on the product’s average customer reviews.
- Availability: This displays to users whether the item is in or out of stock directly on the result.
9. Design for Mobile Friendliness
Google now ranks based on a Mobile First Index. This means that Google is now looking at your site’s performance on mobile before it even looks at its desktop version. You can use the Google Search Console to see how your website operates on mobile devices, and where it needs improvement.
We’ve already covered several things that will improve your online store’s mobile experience. When optimizing your site for mobile devices, follow these guidelines:
- Use the same images and text on both your mobile and desktop site.
- Enable structured data for reviews and products.
- Have title tags, meta descriptions, etc. in place.
- Check your page load time for mobile devices.
- Implement AMP (accelerated mobile pages).
In addition to these guidelines, your site should be using responsive design. When a website is responsive, it dynamically changes to fit the site of the user’s device screen, presenting all necessary elements in a way that works best for that orientation.
10. Include FAQ Section
Many users’ keywords searched are questions. Including a FAQ section in your eCommerce store is a good idea. You can answer common customer questions on the product page and display them in a question-and-answer format.
If you know your customer profile well, you will probably have some idea of the type of questions they ask. If you need help, you can consult your sales team and customer success team. Plus, keyword research tools can guide you and filter the keywords posed as questions.
11. Improve Your Page Speed
Because Google prioritizes websites and eCommerce stores that serve seamless browsing experiences, the loading speed of your website’s pages is a crucial factor in ranking. 40% of consumers will leave a website if they need to wait more than 3 seconds for it to load.
You can easily measure your website pages’ current speed using a tool like PageSpeed Insights. Google says the ideal page loading time should be less than 3 seconds. If your page loads slower than that, you can take the following actions to improve your timing:
- Compress extremely large photos and images.
- Reduce the amount of redirects it takes to get to your page.
- Optimize your server response time (it should be below 200ms).
- Make sure your website is running on top quality hosting.

10. Monitor Your Progress
With your SEO strategies in full effect, it’s crucial to determine what’s going right, what’s going wrong, and where to improve. SEO is not a “set it and forget it” marketing strategy; it’s constantly changing and evolving, requiring your constant attention.
Utilize Google Analytics throughout every SEO change you make to your eCommerce website. Keep an eye on pages that seem to be performing worse than others and use that information to make informed decisions. You may even find out that certain products may need to be altered or discontinued to boost profits gained from your traffic.
Wrapping Up
With the guidelines that we’ve covered, your online store’s SEO strategy can begin. However, keep in mind that this checklist doesn’t cover every single facet of SEO; this only scratches the surface. Using these basics, continue to optimize your online store in new ways that keep Google, and your customers, satisfied.
SEO


Thank you for sharing this article, I`m very appreciative and thankful to read thank you. Keep sharing.
Hi Ken, thank you for the thumbs up! We're very happy to be helpful. ?
Thank you for sharing this information. This information is very useful to us.
Great content. I love how your articles make it easy to understand and implement for people with little or no knowledge of SEO. Keep writing!
Hi Keval, thank you for the wonderful comment! We're so glad to hear we can be helpful, and going to keep sharing content that we think is insightful. Come back for more!
This is a fantastic post on behalf of the SEO Checklist for eCommerce.
Thank you Mattew!
I love this article because all content is too good. Thanks for sharing the awesome article.
Thanks a lot! Come back for more!
Hi, thank you for such a brilliant post. I have been reading some blogs that gives me more knowledge about this topic seo checklist for ecommerce to help you drive organic traffic. I must say this is one of the best among them. You have done a great research for I feel, thanks for sharing.
thanks for the quality articles you post on your blog!!
its a very helpful information for us. thanks for such good information.
Thanks a lot for the comment, we're glad to hear we can be helpful!
Hi Surya, we're really glad to hear you find our blog useful!
Thank you, Aqib!
it is useful information for us. Thanks for share such a good information. ITS my 2nd time I visit here
Reference Keywords in URLs is also useful: Because URL is the first thing Google, and oftentimes users, notice. An easy-to-read URL helps people and search engines understand a page’s context.
Thanks a lot for sharing your knowledge Robert, we appreciate your contribution!
This is great list of resources!
I am glad to know about Rich Snippets. I ever used to see rich snippets on e-commerce sites but didn't know the actual keyword related to whatever you explained in Rich snippets. Thanks.
Thank you, we appreciate it!
Thank you, Brack! We're glad to hear you found the blog informative!
Wow, I’m happy I found this article. I agree with you, put yourself in the customer’s shoes could help us to get the desired results for business i,e, searcher’s intent. I really appreciate your work. Thanks! Looking forward to the next.
Great information and instructions here, I love your content. it gives more knowledge about SEO. Thanks for sharing
Nice! The information I got through this blog has really helped me in understanding this SEO checklist for ecommerce to help you drive organic traffic That was something, I was desperately looking for, thankfully I found this at the right time. Thanks for giving us such useful article.
Absolutely informative article. I read your article and your article is very helpful for me thanks for sharing it with us. It certainly reminded me of so many “ToDo’s” to add to my list.
thanks
Thanks a lot, Ganesh, we're so happy to be helpful!
Thanks a lot, David! It makes us really happy to hear we could be helpful!
That's amazing, Priya! We're happy to share our knowledge!
Thank you for reading!
I was looking for a fresh perspective on this topic, this post was useful. You explained the concepts so well. The company I work for has been discussing ways to attract new customers. Thanks for helping me see how getting SEO right will drive more organic traffic.
Very Informative Article.
Great Piece of Content for E-commerce Stores & easy to understand too.
Very well written article about the checklist for SEO which serves a very important role in search engine optimization.
Thanks for the article.
Thank you so much for this Article. This the exactly what I am looking for it.
Really helpful for people like me who just started eCommerce journey
Very Informative Thanks for Sharing.
It is a great blog post, very helpful and informative tips for eCommerce business. I like it thanks for sharing this information.
Creating a beautiful website is only the 50 percent of the job. Search Engine Optimization is the other 50 percent that leads to success. This article is very helpful for the proper implementation of SEO to our website. Thank you.
Thanks for sharing!
Thankyou so much for sharing
Nice post
Thank you, Erin! We appreciate the comment!
Thank you, Emily!
Thank you, Keerthi, we appreciate it!
Thank you! We appreciate the comment!
Thank you, Anil!
Thank you!
Thanks a lot!
Thank you! We're glad to hear that!
Thank you!
Thank you for reading!
Thank you!
nice post
Thank you for the comprehensive knowledge, really appreciate it.
The points mentioned in this post will help optimise an eCommerce website to further boost its organic traffic. Thanks for sharing such effective content!
Great advice, a lot of people are still stuck in the 2010’s methods of SEO/Marketing. This article is definitely up to date on which methods are working best right now. Thanks for sharing this.
This concept is very good which give us information regarding the seo checklist for ecommerce to help you to drive organic traffic. It is a pleasure worth reading this article. I enjoyed reading this article and would suggest others to come in this particular blog and get all the information regarding it.
SEO is important for every business.
This is very great article. Thank you For sharing with us.
Thanks for sharing such useful information as a blog.
Really like these new tips, which I haven't heard of before, like the Add Content to Pages. Can’t wait to implement some of these as soon as possible.
That makes sense that you would need to fix your title tags. I need more traffic to my website. I'll have to consider getting an SEO marketer to look at my site.
Internal links are the link that direct visitors from one page on your website to another page on your site.
great piece of content and love the fact how the content goes in depth about SEO
Thanks for sharing this content. It's very informative and useful.
Looking forward for more posts like this.
SEO is one of the most important parts of an effective online marketing strategy. With SEO, you can track nearly every aspect of your strategy, like increases in rankings, traffic, and conversions. You even have the ability to see demographic information and other individual engagement metrics.
I read this post your post so nice and very informative post thanks for sharing this post. Creative blog I have ever seen. good work. I appreciate that.
Successful SEO isn't tied in with deceiving Google. It's tied in with partnering with Google to give the best-indexed lists to Google's clients.
Thank you!
I like your services , your packages are really affordable . Thank you for sharing these advices, I hope it will help me
SEO in today's digital marketing is the #1 factor for the business to boom.
Provides valuable insights into queries that your target audience is actually searching on google.
very helpful content.
Thank you for sharing. It is a very interesting and helpful checklist.
Keyword Optimization: Prioritize keyword research to identify relevant terms for your industry. Create high-quality content infused with these keywords to improve organic search visibility. Craft engaging, informative content that seamlessly integrates keywords without compromising readability.
Great checklist! This comprehensive guide is perfect for eCommerce sites looking to boost organic traffic. The actionable tips and clear explanations make it easy to follow and implement. Thanks for sharing such valuable insights!